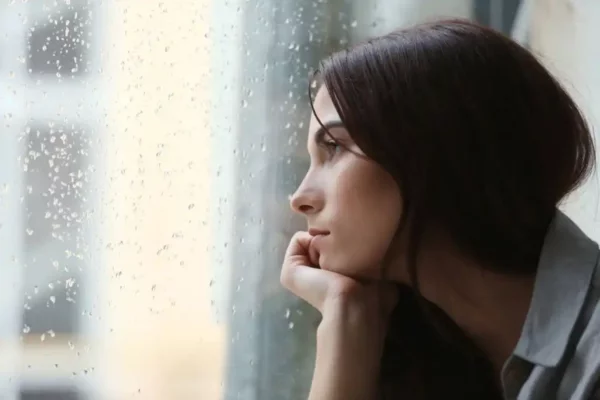
(Exploring Your Mind) Research in the USA has found a link between wisdom, loneliness, and the microbiota in your gut. What do these three things have in common and how do they affect you?
Related Arizona State Senator Wendy Rogers Launches Petition to Decertify the 2020 Election
by Staff Writer, August 3rd, 2021
You’d probably think that wisdom, loneliness, and gut microbiota were completely unrelated to each other. However, a recent study in the field of neuroscience showed that they’re actually closely linked.
The University of San Diego, California (USA) conducted this research. Dr. Tanya T. Nguyen led the study. In fact, it was published in the journal, Frontiers in Psychiatry.
What’s the relationship between wisdom, loneliness, and gut microbiota? Interestingly, the researchers proposed that both wisdom and loneliness are feelings that seem to be heavily influenced by the diversity of microorganisms in the gut. This ratifies the idea of the gut as being the “second brain”
“How sad to think that nature speaks and mankind doesn’t listen.”
-Victor Hugo-

The study
The researchers conducted the study with 184 participants of both sexes. All of them were in good health. They ranged between 28 and 97 years old.
The researchers gave all the participants a questionnaire to assess their levels of loneliness and wisdom. The questionnaire also asked about levels of compassion, social support, and commitment. Furthermore, the participants all provided samples of their excrement. Scientists analyzed these samples in a laboratory.
The researchers were working on the basis of a theory that had been mentioned in previous studies. It proposed that the traits of wisdom correspond to certain regions of the brain. In fact, those who are wiser develop more intense feelings of happiness and well-being. At the same time, those who are less wise tend to feel less comfortable about their life.
In addition, those with more wisdom experience fewer feelings of loneliness. Similarly, those who are lonely tend to be less wise.
The influence of gut microbiota
We formerly knew microbiota as “gut flora”. It’s made up of trillions of microbes that inhabit the digestive tract. These can be bacteria, fungi, or viruses. For a long time, scientists have considered that there exists a gut-brain axis. In other words, that there’s an essential link between the two organs. Consequently, intestinal function influences the emotional and cognitive centers of the brain and vice versa.
Alterations in the gut-brain axis can cause deficiencies in stress responses, moods, and decision-making, among other processes. Furthermore, scientists discovered that microbiota has an impact on mental health disorders. For example, depression and anxiety.
Before they conducted the University of California study, scientists had already found evidence that suggested people who had a more active and diverse social life also had more varied microbiota. The University of California researchers followed on from this information. Their results turned out to be extremely interesting.
The results
To establish the relationship between wisdom, loneliness, and intestinal microbiota, the researchers compared the questionnaire results with the analyses of the excrement. Although it may seem rather bizarre, this meant they were able to establish whether there was a relationship between the two elements.
The scientists measured microbial diversity in two ways. The first was alpha-diversity. This concerned the ecological richness of the microbe species in each individual. The second was beta-diversity. This concerned the diversity in the composition of the community of microbes.
The results suggested that:
- People with lower levels of loneliness and higher levels of wisdom had an ecologically richer and more diverse population of microbes.
- People with reduced diversity of microbes experienced poorer mental and physical health.
- The more diverse the microbiota, the less likely it is that pathogens will invade.
Conclusion
Scientists don’t know why there’s a link between wisdom, loneliness, and intestinal microbiota. In fact, they’re unsure as to how psychological and biological factors interact. Perhaps a poor mental state affects the microbiota. However, it could be the other way around. Nevertheless, they’ve certainly found definite evidence in support of the relationship between these three factors.
Please consider becoming a $10 a month donor. (Donate HERE)
Stillness in the Storm Editor: Why did we post this?
The news is important to all people because it is where we come to know new things about the world, which leads to the development of more life goals that lead to life wisdom. The news also serves as a social connection tool, as we tend to relate to those who know about and believe the things we do. With the power of an open truth-seeking mind in hand, the individual can grow wise and the collective can prosper.
– Justin
Not sure how to make sense of this? Want to learn how to discern like a pro? Read this essential guide to discernment, analysis of claims, and understanding the truth in a world of deception: 4 Key Steps of Discernment – Advanced Truth-Seeking Tools.
Stillness in the Storm Editor’s note: Did you find a spelling error or grammatical mistake? Send an email to [email protected], with the error and suggested correction, along with the headline and url. Do you think this article needs an update? Or do you just have some feedback? Send us an email at [email protected]. Thank you for reading.
Source:
https://exploringyourmind.com/wisdom-loneliness-and-gut-microbiota-are-linked/
Support our work! (Avoid Big Tech PayPal and Patreon)DIRECT DONATION

Leave a Reply