(Andy Corbley) When it comes to broken bones, the children of generation Z may never have to deal with the itching that comes from wearing a cast—an all-too-familiar scenario for both kids and adults healing from accidents.
Related The Comfortable Misery Syndrome: Why People Choose Misery Over Change
by Andy Corbley, July 10th, 2020
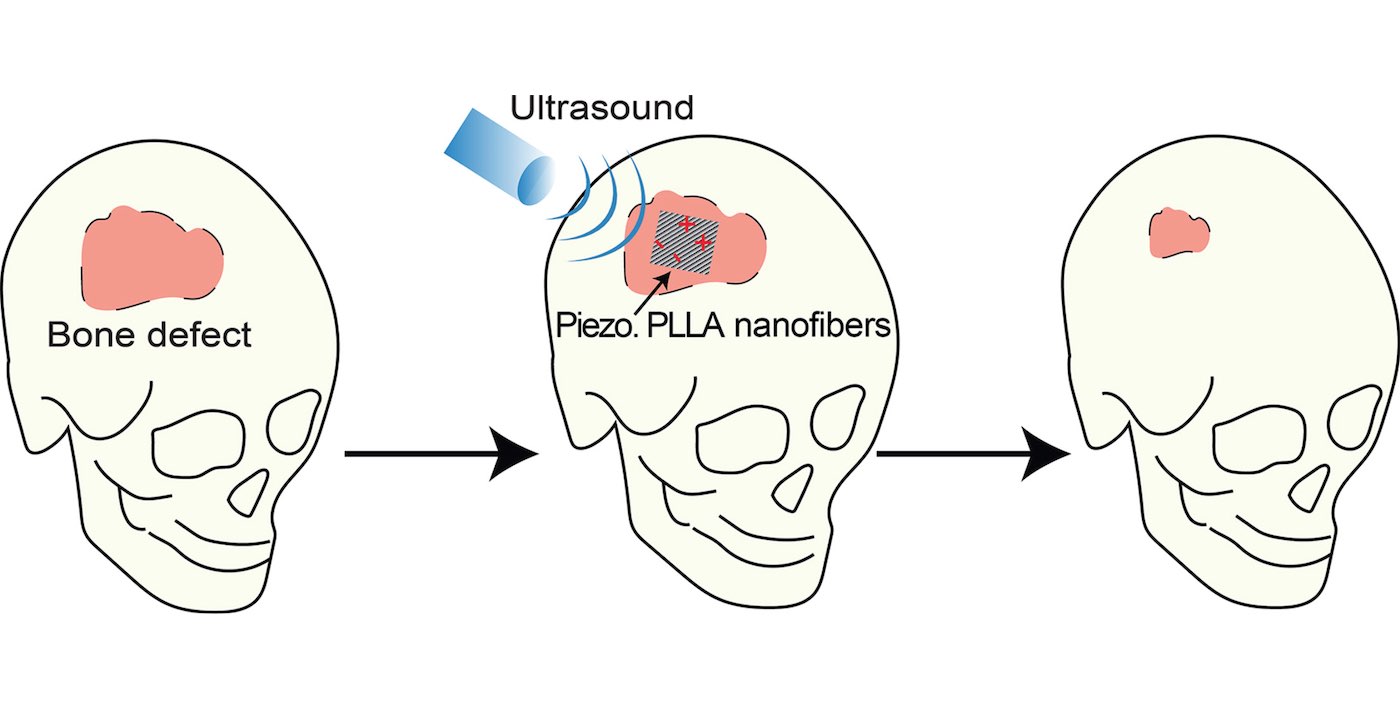
Instead, doctors may, in the near future, be able to repair broken bones by encasing the fracture in a field of electricity, which would be especially welcome for treating body parts, such as the scull, where casts don’t work.
A group of biomedical engineers from the University of Connecticut have invented a scaffold of non-toxic polymer that also generates a controllable electrical field to encourage bone growth. The researchers published a paper in Nano Energy after using their device to cure skull fractures in mice.
The scaffold mimics the natural electric field produced by our bodies, a characteristic called piezoelectric, meaning to generate electricity from vibrations, and can be affixed over the damaged bone without significant surgery.
The patient can wave an ultrasound wand over the area to stimulate the generation of electricity and, unlike similar existing machines that are bulky and require electricity from a power outlet or batteries, the device is lightweight and generates the field via ultrasound.
The polymer from which the device is made is non-toxic and gradually dissolves in the body over time, disappearing as the new bone grows.
Book Healing is Voltage: The Handbook, 3rd Edition
“The electric field created by the piezoelectric PLLA scaffold seems to attract bone cells to the site of the fracture and promote stem cells to evolve into bone cells. This technology can possibly be combined with other factors to facilitate regeneration of other tissues, like cartilage, muscles or nerves,” says Ritopa Das, a graduate student at Nguyen Research Group and the first author of the published paper.
The device’s proof of efficacy is a case of leaping before looking, as scientists aren’t exactly sure why electrical fields stimulate bone growth at all.
Bone itself is somewhat piezoelectric, generating a surface charge when the bone is stressed by everyday life activities. That surface charge encourages more bone to grow. But scientists don’t know whether it’s because it helps cells stick to the surface of the bone, or whether it makes the cells themselves more active.
About The Author
Andy Corbley is the founder and editor of World At Large, a small environment, travel, and lifestyle focused journal that stresses integrity, nuance, and honesty which launched in early March 2019.
Stillness in the Storm Editor: Why did we post this?
The news is important to all people because it is where we come to know new things about the world, which leads to the development of more life goals that lead to life wisdom. The news also serves as a social connection tool, as we tend to relate to those who know about and believe the things we do. With the power of an open truth-seeking mind in hand, the individual can grow wise and the collective can prosper.
– Justin
Not sure how to make sense of this? Want to learn how to discern like a pro? Read this essential guide to discernment, analysis of claims, and understanding the truth in a world of deception: 4 Key Steps of Discernment – Advanced Truth-Seeking Tools.
Stillness in the Storm Editor’s note: Did you find a spelling error or grammatical mistake? Send an email to [email protected], with the error and suggested correction, along with the headline and url. Do you think this article needs an update? Or do you just have some feedback? Send us an email at [email protected]. Thank you for reading.
Source:
Leave a Reply