(Ivan) Researchers have recently discovered the entrance to a network of underground passages near the north pole of the Moon. These entrances could facilitate future Astronauts easier access to potential sources of water in the subsoil of our natural satellite.
Source – Ancient Code
by Ivan
SETI marks the X
The SETI Institute, dedicated to the search for life outside the Earth, and the Mars Institute, focused on the promotion of the study of Mars, have announced the discovery of small entrances that may lead into an underground network of lava tubes in a large crater near the North Pole of the Moon.
These “entrances” could allow future explorers to easier access water ice on the moon if it there are accumulations of it inside these passages. This would also mean that astronauts would not need to go through an enormous effort to excavate regoliths, the debris that covers the lunar terrain.
The entrances were identified thanks to a thorough analysis of images taken by the Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter (LRO).
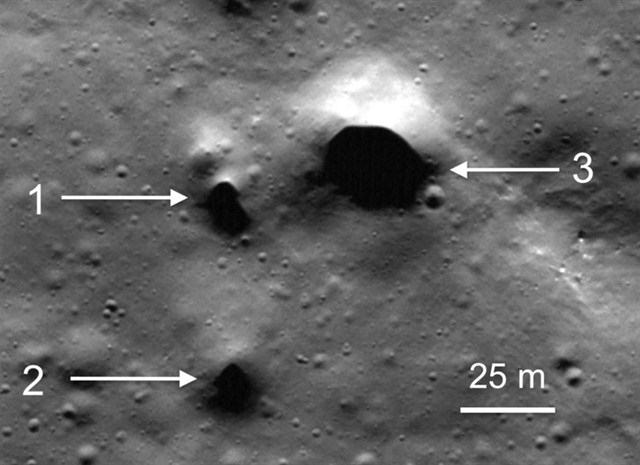
The underground passages are located northeast of Philolaus, a large impact crater 70 km in diameter located around 550 km from the lunar north pole.
These shafts appear as small borderless depressions, 15 to 30 meters wide, with completely shaded interiors.
They are located along sections of winding canals known on the Moon as “sinuous rilles,” that crisscross the floor of Philolaus Crater. Lunar sinuous rilles are generally thought to be collapsed, or partially collapsed, lava tubes, underground tunnels that were once streams of flowing lava, explains an article by SETI.
“The highest resolution images available for Philolaus Crater do not allow the pits to be identified as lava tube skylights with 100 percent certainty, but we are looking at good candidates considering simultaneously their size, shape, lighting conditions and geologic setting” says Pascal Lee, planetary scientist at the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute who made the new finding at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley.
Philolaus Traverse from SETI on Vimeo.
They are located along sections of winding canals known on the Moon as “sinuous rilles,” that crisscross the floor of Philolaus Crater. Lunar sinuous rilles are generally thought to be collapsed, or partially collapsed, lava tubes, underground tunnels that were once streams of flowing lava, explains an article by SETI.
“The highest resolution images available for Philolaus Crater do not allow the pits to be identified as lava tube skylights with 100 percent certainty, but we are looking at good candidates considering simultaneously their size, shape, lighting conditions and geologic setting” says Pascal Lee, planetary scientist at the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute who made the new finding at NASA’s Ames Research Center in Silicon Valley.
Polar Caves on the Moon? – Pascal Lee from SETI on Vimeo.
Experts note that prior to this discovery, previous studies had found more than 200 pits on the Moon, many of which have been identified as possible skylights that lead to underground lava tubes associated with similar sinuous furrows. However, the new discovery represents the first published report of possible lava tube skylights in the Selenite polar regions, according to its authors.
What makes the discovery even more appealing is the fact that since Philolaus is located on the near side of the moon, its position affords direct communications with the Earth.
“We would also have a beautiful view of Earth. The Apollo landing sites were all near the Moon’s equator, such that the Earth was almost directly overhead for the astronauts. But from the Philolaus skylights, Earth would loom just over the crater’s mountainous rim, near the horizon to the southeast” said Pascal Lee, a planetary scientist at the SETI Institute and the Mars Institute.
Ivan is editor-in-chief at ancient-code.com, he also writes for Universe Explorers. You may have seen him appear on the Discovery and History Channel.
_________________________
Stillness in the Storm Editor’s note: Did you find a spelling error or grammar mistake? Do you think this article needs a correction or update? Or do you just have some feedback? Send us an email at [email protected] with the error, headline and url. Thank you for reading.
Leave a Reply